Hookworms are parasitic creatures that cause intestinal disease in humans. They enter the body through the skin of the feet and then travel through blood vessels to the heart and lungs. The larvae then attach to the walls of the small intestine. There, they grow and mature. They can live for two years inside the body.
What Is Hookworms?
Hookworm infections are a major concern for people living in warm, moist climates or in areas with poor hygiene and sanitation. Hookworm larvae can be carried in human feces and can infect humans through contact with the soil. Infected individuals may also infect the soil through defecating outdoors and using human feces as fertilizer. Furthermore, children who play in contaminated soil are at risk of contracting hookworm infections.
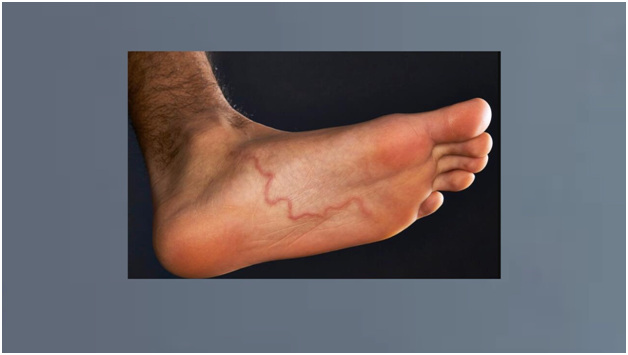

Hookworm larvae enter the human body via the skin of the feet and travel up the respiratory system, where they are often swallowed or coughed up. In the small intestine, they develop into adults and feed on human blood. They can live for two years in the body. The hookworm infection is diagnosed by looking for the presence of hookworm eggs in stools. Ideally, stool samples should be examined within several hours after defecation.
What are human symptoms of hookworms?
Human hookworm infections can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from diarrhea to GI discomfort. In some cases, people may even develop anorexia, an ailment characterized by weakness and fatigue. These symptoms peak about 30 days after the hookworm infection has taken place. Mild infestations may not cause any symptoms at all. However, severe cases can result in severe blood loss. In addition, hookworms can cause anemia.
Hookworms are an intestinal parasite that is common in tropical climates. They typically develop after coming into contact with soil that has been contaminated with human feces. Once inside the body, hookworm larvae burrow into the blood stream, and then migrate to the lungs and air sacs. From there, they crawl up the air sacs and lungs before maturing into adult hookworms inside the bowel. If you develop these symptoms, it is best to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How do you test for hookworms in humans?
Hookworm infections are a nuisance that can be extremely dangerous if left untreated. This parasitic infection can lead to anemia, protein deficiency, and more serious conditions. According to the CDC, between 576 million and 750 million people worldwide are infected with hookworms. Though cases of hookworm have declined in recent decades, this infection can affect anyone, including pregnant women, children, and people with weakened immune systems. As such, it is extremely important to test yourself for hookworms if you have suspected contact with hookworm larvae.
Hookworms enter the body through the skin and then move through the bloodstream. Once inside, they attach themselves to the walls of the small intestine and continue their growth and development. They can remain in the body for two years or more. This is why a stool sample is important in diagnosing hookworm infection.
Treat hookworms with ivermectin
Using ivermectin to treat hookworms in marine mammals can be an effective way to reduce infestations. One study found that the drug reduced infestations in Australian sea lions by more than 80 percent. This medicine is also an effective treatment for human hookworm infections.
The drug targets ligand-gated chloride ion channels found in muscle and nerve cells of invertebrates. This binding action increases the permeability of the cell membrane, which ultimately leads to paralysis and death of the parasite. The drug is also believed to act as an agonist of GABA, a neurotransmitter that regulates neurosynaptic transmission. In addition, ivermectin inhibits development of O. volvulus microfilaria and may inhibit its release from the uterus.
Although hookworms are generally not visible, some people are at a greater risk of contracting the infection after traveling to tropical areas. The good news is that a new class of oral antihelmintic drugs are now available that are safe and effective. These drugs are often well tolerated and are effective in treating hookworm infections.
Which precaution is appropriate for hookworm?
Providing periodic hookworm medication to people living in infected areas is an important part of the prevention of the disease. The medication is administered by community health workers or healthcare providers who visit households to deliver it. Other preventative measures include avoiding skin contact with soil, and avoiding consuming soil-contaminated foods. While most people will not experience any symptoms at first, infection with hookworm can have serious consequences for the body.
Hookworm infections occur as a result of the infestation of a nematode in the small intestine. While the most common nematode is Necator americanus, there are other forms of hookworm as well. They belong to a category of parasites known as soil-transmitted helminths.


