Anxiety disorders are characterized by continual fear and worry that does not disappear or worsens over time. Anxiety disorders are common in people with high blood pressure and can harm their health. Heart disease refers to several conditions that might damage the heart and blood vessels.
The Relation Among Heart Disease & Anxiety Disorders
According to research, both heart disease and anxiety disorders can cause the development of the other. Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), increase your risk of heart disease by 26%, particularly coronary artery disease and heart failure.


Long-term anxiety causes changes in the body, including decreased blood flow to the heart, increased blood pressure and heart rate, and increased levels of cortisol, a stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands. These effects can eventually cause heart problems.
According to research, anxiety disorders lead to heart disease in a variety of ways, including:
- Inflammation:-
Anxiety and anxiety disorders are linked to higher inflammatory markers, indicating a high level of inflammation in the body.
- Endothelial dysfunction:-
The layer of cells which forms the lining of blood vessels (vascular endothelium) is critical to the circulatory system’s health and maintenance. Anxiety and anxiety disorders have been linked to vascular endothelial changes linked to inflammation, blood clots, and the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Platelet dysfunction:-
Blood cells called platelets are in charge of causing blood to clot. More significant platelet aggregation occurs in those who are anxious or under intense stress, which can cause irregular blood clotting and heart attacks.
An anxiety condition can start to develop due to a heart attack. About 30% of persons who have had a heart attack may experience increased anxiety in the days and weeks that follow the attack. This anxiety may be brought on by the heart attack itself, the worry about dying or being disabled, or the expense of receiving medical attention.
Also read: 7+ Home Remedies To Cure Migraine
A person experiencing an anxiety attack may exhibit symptoms similar to anyone experiencing a heart attack, such as:

- chest pain
- Dizziness
- Numbness in the hands and feet
- Breathing difficulty
- Trembling
- Irregular heartbeats
You can do CT Coronary Angiography Test From BookmeriLab to diagnose the cause of chest pain or other symptoms. The CT Coronary Angiography (CCTA) scanning checks at blockages and irregularities in the heart’s blood-supply vessels.
Anxiety and Heart Disease Complications
People with heart disease and anxiety are more likely to have poorer outcomes, such as severe disability or death, than people with heart disease who are not anxious.
Anxiety can also cause you to be concerned about your health. Your fears may prevent you from sticking to your treatment plan.
Despite conflicting evidence, anxious people appear less likely to engage in healthy behaviours that may help with heart disease. Worried people consume more cholesterol, eat more food, live sedentarily, and work out less.
Anxious people are also less likely to attend and finish cardiac rehab programs. These behaviour factors can increase the risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in people with anxiety disorders.
Anxiety is also linked to a lower likelihood of following risk-reduction recommendations after a cardiac arrest, such as stopping smoking, using social support, and reducing stress.
Anxiety and Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosis of anxiety disorders in people with cardiovascular disease is difficult because the symptoms of anxiety disorders and heart disease overlap significantly.
Accurate diagnosis is required for the effective treatment of these disorders. Your primary care doctor can diagnose anxiety disorders and heart diseases, but treatment may be referred to a mental health professional and a cardiologist.
Your doctor may order the following tests to diagnose heart disease:
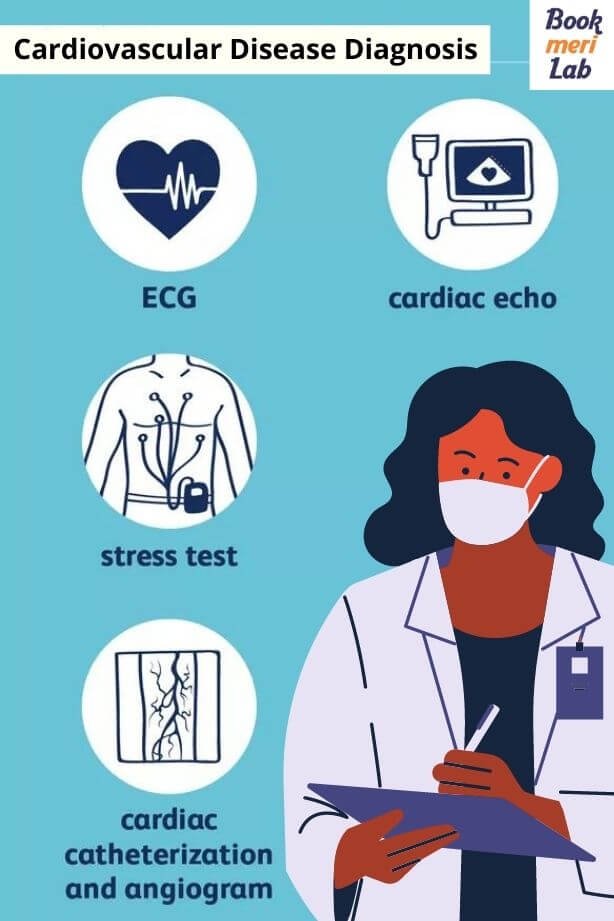

- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG):
This test detects electrical activity in the heart. Your doctor will look for specific patterns to determine whether or not your heart is abnormal.
- Echocardiogram:
An ultrasound of the heart is used in this test. A small probe (a transducer) is placed on your chest numerous times to generate an image of your heart.
- Stress test:
Doctors will measure your heart rate to understand your heart health better. During this test, you will be asked to wear a blood pressure monitor while running or walking on a bicycle or treadmill. Additionally, an EKG will be connected to you. If you are unable to tolerate exercise for the test, medications can be used to raise your heart rate and simulate normal heart responses to exercise.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan:
A unique dye is put into your body during this test, and imaging scans using it can show specific physical issues.
- Nuclear stress test:
This test uses imaging to look at your heart before and after exercise to determine how much physical stress it has undergone.
Treatment of Heart Disease and Anxiety


Medications:-
The medications you may require to treat heart disease will vary based on the particular condition, but they may include:
- Diuretics help the body eliminate extra salt and fluid
- Beta-blockers are used to treat irregular heartbeats
- Statins are cholesterol-lowering medications.
Anxiety is generally treated with medications and psychotherapy. Anxiety medications include the following:
Anti-Anxiety Medications:- These medications can help relieve stress, panic disorder, and severe fear and worry. The most widely used anti-anxiety drugs are benzodiazepines.
Antidepressants:- Anxiety is commonly treated with antidepressant medications known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). They may help your brain use certain chemicals that control your mood or stress better.
Changes in Lifestyle
Because diet affects the development and progression of both disorders, dietary adjustments can be helpful for anxiety and heart disease.
Taking whole foods that are high in nutrients and vitamins while avoiding foods that cause inflammation, such as deep-fried foods, high-fat foods, and processed foods, is helpful for both heart disease and anxiety.
Stress can be relieved by managing your stress levels through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing. Regular exercise can also help relieve stress. According to research, people who work out regularly have lower anxiety levels.
Exercise can also help manage blood pressure, lower cholesterol, and strengthen the heart muscle in people with heart disease.
Conclusion:-
Anxiety and heart disease are closely related. Individuals suffering from stress are more likely to acquire heart disease than those who do not. On the other hand, after a heart attack, those with heart disease are more prone to develop an anxiety disorder. You can better manage your heart disease and anxiety by getting the therapy and support you need after obtaining a correct diagnosis.


